Click on RISK ASSESSMENT
PORTAL to know your Madhumeha (Diabetes) Risk Level
Click on RISK ASSESSMENT
PORTAL to know your Madhumeha (Diabetes) Risk Level









 Click on RISK ASSESSMENT
PORTAL to know your Madhumeha (Diabetes) Risk Level
Click on RISK ASSESSMENT
PORTAL to know your Madhumeha (Diabetes) Risk Level







Pharmacovigilance is the science dedicated to reduce the risk of drug-related harms to patients. In India, National Pharmacovigilance Program under the control of Central Drug Standards Control Organization (CDSCO) has initiated during 2003. WHO emphasizes that, traditional medicines are to be included into pharmacovigilance system and has published guidelines on safety monitoring of herbal medicines in pharmacovigilance systems in 2004.
The nationwide programme under central sector scheme funded by Ministry of AYUSH, New Delhi for ASU & H drugs to establish and manage a data base of Adverse Drug Reactions (ADR) for developing system wise database of adverse drug reactions and evolving evidence based recommendations towards clinical safety of ASU & H Drugs. Besides this; the program also undertake surveillance of objectionable or misleading advertisements.
Since ages Ayurveda, Siddha and Unani systems are being practised in India. In this era of globalization, concerns are being raised with regards to their clinical safety. Ayurveda has categorized toxic plants separately and for their use special processing is essential. There is a wide spread misconception that all drugs of “natural” origin are “safe”. There is also a common belief that long term use of a medicine based on tradition, assures both safety and efficacy. Further when ASU & H medicines are used in conjunction with other medicines, there is a possibility of drug interactions. There are also examples of ASU & H medicines being adulterated or contaminated with allopathic medicines, chemicals such as corticosteroids, non-sterodial anti-inflammatory agents etc. Further many ASU & H drugs are manufactured for global use and they have moved beyond the traditional and cultural framework for which they were originally intended. Currently, majority of adverse events related to the use of herbal / traditional products that are reported are attributed either due to poor product quality or to improper use.
ASU & H systems of medicines have their own principles and have their own pharmacopoeia, but at times even are practised in the country as OTC drugs without any authentic prescription. Considering the growing use of ASU & H products and medicines globally; inclusion of traditional medicines in Pharmacovigilance systems became equally important. Pharmacovigilance is defined as the detection, assessment and prevention of adverse drug reactions in humans.
Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India, New Delhi has initiated the Pharmacovigilance Program for ASU & H drugs. Worldwide movement for the improvement of patient safety gains momentum, the subject of drug safety becomes even more prominent. Pharmacovigilance is the science dedicated to reduce the risk of drug-related harms to the consumers. Looking into the conditions prevailing in the present scenario, it is high time to deliberate regarding the concerns over traditional and classical Ayurvedic, Siddha, Unani and Homoeopathy products and practices. Thus the program is initiated to collect, collate and analyze data to establish evidence for clinical safety of ASU & H drugs in a scientific manner for documenting clinical evidence of safety and to undertake surveillance of misleading advertisements of ASU & H drugs and improper advertisements of ASU & H drugs for regulatory actions.
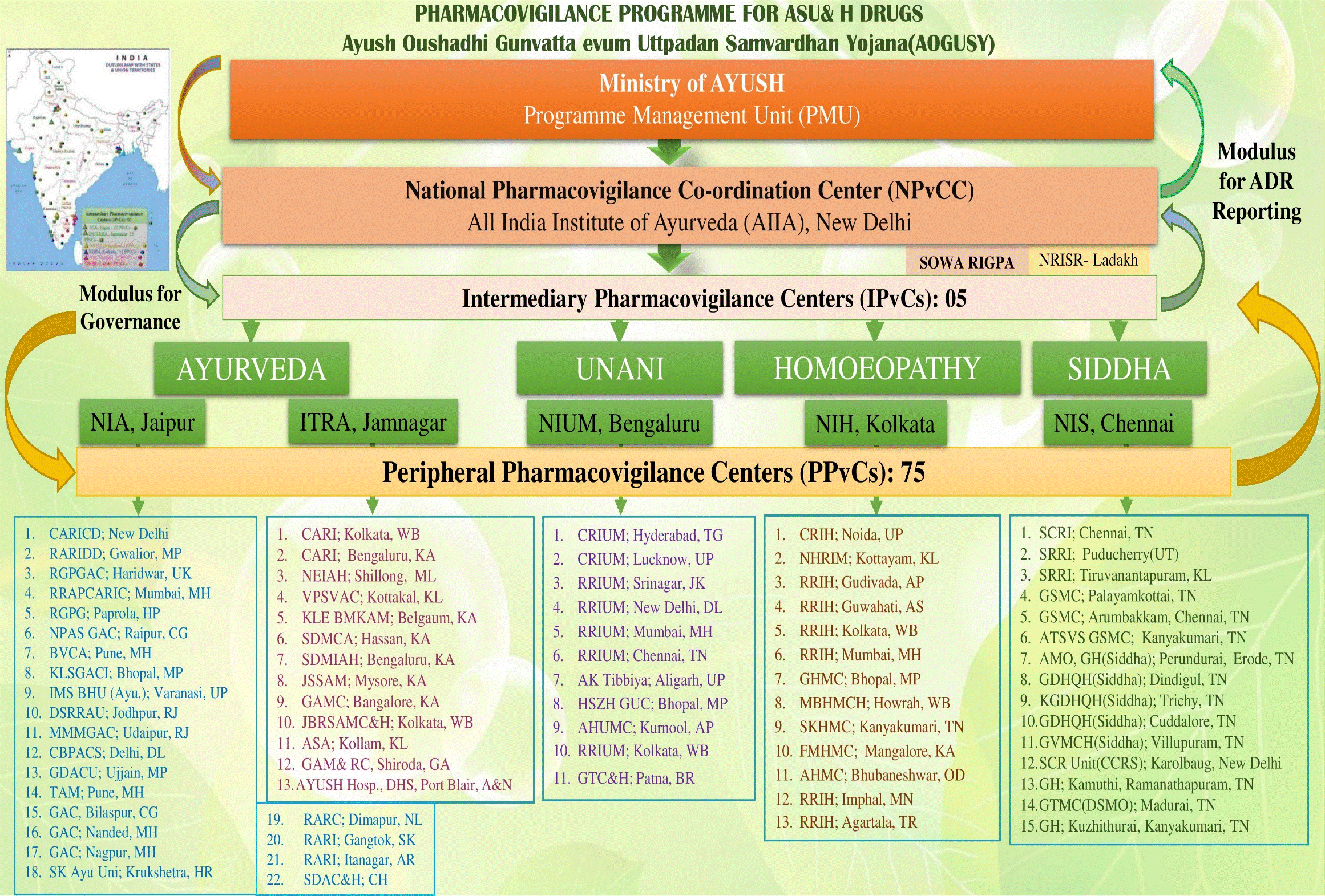
The program shall be coordinated by NPvCC under the supervision of Ministry of AYUSH, New Delhi that would monitor the program and also recommend regulatory interventions based on the generated Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) data and objectionable advertisements.

The nationwide programme under central sector scheme funded by Ministry of AYUSH, New Delhi for ASU & H drugs to establish and manage a data base of Adverse Drug Reactions (ADR) for developing system wise database of adverse drug reactions and evolving evidence based recommendations towards clinical safety of ASU & H Drugs. Besides this; the program also undertake surveillance of objectionable or misleading advertisements.

Secondary pharmacovigilance centres, acting as second level centres in the administrative structure of the program. Five National Institutes (National Institute of Ayurveda, Jaipur; Institute of Teaching and Research in Ayurveda, Jamnagar; National Institute of Siddha, Chennai; National Institute of Unani Medicine, Bengaluru; and National Institute of Homoeopathy, Kolkata) are designated as Intermediary Pharmacovigilance Centres.

Primary pharmacovigilance centres. They are relatively smaller ASU & H colleges or institutions including. These are the first contact ADR data collection units. They would be identified and coordinated by IPvCs in consultation with NPvCC.

Designated in-charge of a particular participating pharmacovigilance centre

A healthcare professional involved in investigation of drug related adverse events.

Any person who suspects to have experienced / observed an ADR and informs any participating Pharmacovigilance centre about it.

A healthcare professional reporting ADR on the ADR form.

The process of overseeing drug related adverse events at the Pharmacovigilance centre participating in the Pharmacovigilance Program.

The process of providing ADR information by filling in the ADR form appropriately and forwarding the same to the appropriate level.

Process of informing by a notifier to any participating pharmacovigilance centre about the occurrence of a suspected ADR. The process may involve informing over telephone, in person, email, fax or any other means of communication-verbal or written. All notifiers must give their contact details. Appropriate and adequate measures must be taken to keep track of the notifier. Any follow up action will be initiated on a notification only after the due verification of the notifier. If the notifier cannot be traced back, it will be recorded on the notification slip before closing the case.

A pre-designed structured form for communication of a suspected ADR by the notifier duly signed by him / her.

It’s the pre-designed structured form issued to record suspected ADR.

A systematic and independent examination (conducted by personnel, independent of the centre) of centre’s activities and documents to determine whether centre’s activities were conducted and the data were recorded, analysed and accurately reported according to the protocol and regarding performance of pharmacovigilance centre’s participation in Pharmacovigilance Program for ASU & H drugs.

In a confidential / secretive manner.

Any unintended effect of a pharmaceutical product occurring at doses normally used in man which is related to the pharmacological properties of the drug.

Any untoward medical occurrence that may present during treatment with a pharmaceutical product but which does not necessarily have a causal relationship with this treatment.

Reported information on a possible causal relationship between an adverse event and a drug, the relationship being unknown or incompletely documented previously. Usually more than a single report is required to generate a signal, depending upon the seriousness of the event and the quality of the information.

WHO Technical Report No 498 (1972); ‘A response to a drug which is noxious and unintended, and which occurs at doses normally used in man for the prophylaxis, diagnosis, or therapy of disease, or for the modification of physiological function.

An adverse reaction, the nature or severity of which is not consistent with domestic labelling or market authorization, or expected from characteristics of the drug.

A serious adverse event or reaction is any untoward medical occurrence that at any dose.


A clinical event, including laboratory test abnormality, occurring in a plausible time relationship to drug administration, and which cannot be explained by concurrent disease or other drugs or chemicals. The response to withdrawal of the drug (de-challenge) should be clinically plausible. The event must be definitive pharmacologically or phenomenologically, using a satisfactory re-challenge procedure if necessary.

A clinical event, including laboratory test abnormality, with a reasonable time sequence to administration of the drug, unlikely to be attributed to concurrent disease or other drugs or chemicals, and which follows a clinically reasonable response on withdrawal (de-challenge). Re-challenge information is not required to fulfil this definition.

A clinical event, including laboratory test abnormality, with a reasonable time sequence to administration of the drug, but which could also be explained by concurrent disease or other drugs or chemicals. Information on drug withdrawal may be lacking or unclear.

A clinical event, including laboratory test abnormality, with a temporal relationship to drug administration which makes a causal relationship improbable, and in which other drugs, chemicals or underlying disease provide plausible explanations.

A clinical event, including laboratory test abnormality, reported as an adverse reaction, about which more data is essential for a proper assessment or the additional data are under examination.

A report suggesting an adverse reaction, which cannot be judged because information is insufficient or contradictory, and which cannot be supplemented or verified.

Various causality terms are in use but the following are used most widely. Some, however, do not use all the terms, for instance many do not believe that a ‘certain’ classification is possible for a single report and other make no distinction between ‘probable’ and ‘possible’. These definitions are however acceptable to Programme members who do use the terms. Where only ‘possible’ or ‘unlikely’ are used to describe reactions it must be understood that ‘possible’ include those reactions which are called by others ‘probable’ and ‘certain’, as well as ‘possible’. Whilst ‘conditional / unclassified’ and ‘unassessable / unclassifiable’ are not causality terms, they describe the status of adverse reaction reports and therefore allow for practical communication about ADR issues.

Whenever possible, an estimate of frequency should be provided, expressed in standard category of frequency. It is always difficult to estimate incidence on the basis of spontaneous reports, owing to the uncertainty inherent in estimating the denominator and degree of under-reporting. However, whenever possible, an estimate of frequency should be provided and in a standard form. The following standard categories of frequency are recommended:
| Very common | > 1/10 | (> 10%) |
| Common (frequent) | > 1/100 and < 1/10 | (> 1% and < 10%) |
| Uncommon (infrequent) | > 1/1,000 and < 1/100 | (> 0.1% and < 1 %) |
| Rare | > 1/10,000 and < 1,000 | (> 0.01% and < 0.1%) |
| Very rare | < 1/10,000 | (< 0.01%) |

All India Institute of Ayurveda, New Delhi is the National Pharmacovigilance Co-ordination Centre (NPvCC) for implementation of the pharmacovigilance program for ASU & H Drugs. The NPvCC will receive inputs in terms of suspected ADRs from the Intermediary Pharmacovigilance Centres (IPvCs), which will initially include:
Pharmacovigilance is the science dedicated to reduce the risk of drug-related harms to the consumers. Looking into the conditions prevailing in the present scenario, it is high time to deliberate regarding the concerns over traditional and classical Ayurvedic, Siddha, Unani and Homoeopathy products and practices. Thus, the program is initiated to collect, collate and analyze data to establish evidence for clinical safety of ASU & H drugs in a scientific manner for documenting clinical evidence of safety and to undertake surveillance of misleading advertisements of ASU & H drugs for regulatory actions.
The National Pharmacovigilance Co-ordination Centre (NPvCC) will undertake the pharmacovigilance activities under the guidance and technical support of Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (WHO Collaborating Centre for Pharmacovigilance), Ghaziabad and Concerned programme officers at WHO Country Office-India, New Delhi. The National Pharmacovigilance Co-ordination Centre (NPvCC) in consultation with the Pharmacopoeial Commission of Indian Medicine and Homoeopathy (PCIM&H), if required, shall conduct the Causality Assessment of the signals received from the Intermediary Pharmacovigilance Centres (IPvCs) and intimate to the Ministry of AYUSH regarding confirmed ADRs and misleading advertisements to enable suitable action.

Though for centuries ASU & H drugs are considered as safe and innocuous drugs, this perception is likely to change in light of some recent incidences of ADRs during their use. This along with increased use of ASU & H drugs both at national and international levels is likely to lead to increased interaction of these drugs with diverse genomic profiles. This is likely to increase incidences of expression of unexpected effects, which may be useful or adverse in nature. Thus, it should be considered as the right time to evolve a mechanism to record ADR of ASU & H drugs. Since, there are considerable social and economic consequences of adverse drug reactions and the positive benefit / cost ratio of implementing appropriate risk management – there is a need to engage healthcare professionals and the public at large, in a well-structured programme to build synergies for monitoring adverse drug reactions of ASU & H medicines. The Purpose of the Pharmacovigilance initiative for ASU & H drugs is to collect, collate and analyze data to establish evidence for clinical safety of ASU & H drugs and undertake surveillance of misleading advertisements of these drugs.

ASU & H systems of medicines have their own principles and have their own pharmacopoeia, but at times even are practised in the country as OTC drugs without any authentic prescription. Considering the growing use of ASU & H products and medicines globally; inclusion of traditional medicines in Pharmacovigilance systems became equally important. Pharmacovigilance is defined as the detection, assessment and prevention of adverse drug reactions in humans.


This program for ASU & H drugs shall encourage reporting of all suspected drug related adverse events, including those suspected to have been caused by interaction with any other drugs or food incompatibilities using Suspected Adverse Drug Reaction Reporting Form for ASU & H Drugs. The reporting of seemingly insignificant or common adverse reactions would be important since they may highlight a widespread prescribing problem.

This program for ASU & H drugs shall encourage reporting of all suspected drug related adverse events, including those suspected to have been caused by interaction with any other drugs or food incompatibilities using Suspected Adverse Drug Reaction Reporting Form for ASU & H Drugs. The reporting of seemingly insignificant or common adverse reactions would be important since they may highlight a widespread prescribing problem.



The reporting on prescribed format can be submitted to the nearby / concerned PPvCs / IPvCs.

The information in the form shall be handled in confidentiality. Peripheral Pharmacovigilance Centres shall forward the form to the respective Intermediary Pharmacovigilance Centres who will carry out the causality analysis. This information shall be forwarded to the National Pharmacovigilance Centre. The data will be analysed and forwarded to the Ministry of AYUSH, Govt. of India.

The objective of this skill development programme is to enhance Pharmacovigilance Knowledge and skills of the health care professionals, which in turn promote patient safety. This skill certification scheme aims to enable and mobilize young healthcare professionals to take up training and develop skill in Pharmacovigilance of medical products in ASU&H, which will boost the productivity and standadization of madicens

Ministry of Ayush has been receiving written and online complaints of misleading advertisements of Ayush medicines including herbal medicines/products. Such complaints are also registered in the GAMA (Grievances against Misleading Advertisements) portal maintained by the Department of Consumer Affairs (DoCA). About 809 complaints of advertisements pertaining to Ayush and herbal medicines/products have been received during the period from April, 2015 to March, 2018.Advertising Standards Council of India (ASCI), with whom Ministry had signed a MoU for suo moto monitoring of Ayush advertisements appearing in print and TV media, reported 732 complaints in the period from 20th January, 2017 to 19th January, 2018. Six states/UTs including Delhi, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Kerala, Karnataka and Chandigarh have reported 573 instances of such misleading advertisement during the last three years.
The provisions of Rule 158-B of the Drugs & Cosmetics Rules, 1945 provide for pilot studies for generating proof of safety and effectiveness for grant of license to manufacture for sale certain categories of Ayurveda, Siddha and Unani drugs. As such the terms ‘herbal medicines’ and ‘clinical trials’ are not provided or prescribed in the provisions of Drugs & Cosmetics Act, 1940 and Rules there under pertaining to ASU drugs but certain complaints received in the Ministry referred to these aspects. Two incidents of death have come to the notice of Ministry of AYUSH after consuming herbal medicines/products, one in Tamil Nadu and one in Kerala.
In order to check the veracity of misleading advertisements and claims of AYUSH products, the Central Government has taken following steps-
State Governments have been directed for appointing Gazetted Officers under section 8 (1) of the Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act, 1954 to enter, search any premises or examine or seize any record which contravenes any provisions of the Act. About 621 Gazetted Officers for this purpose are reported to have been appointed in 22 states.
Complaints of misleading advertisements of Ayurvedic, Siddha, Unani and Homoeopathic medicines are forwarded to the concerned State Licensing Authorities for action in accordance with the provisions of Drugs & Cosmetics Act,1940 and Rules thereunder and Drugs & Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act, 1954 and Rules thereunder.
Ministry of AYUSH signed MoU with Advertising Standards Council of India (ASCI) to undertake monitoring of the misleading AYUSH –related advertisements appearing in print and TV media and bring the instances of improper advertisements to the notice of the State Regulatory Authorities for taking necessary action. On the request of Ministry of AYUSH, Ministry of Information & Broadcasting issued an advisory to all media channels to ensure strict compliance of the provisions of Drugs & Cosmetics Act, 1940 and Drugs & Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act, 1954 in respect of AYUSH health products/drugs being advertised. TV channels have been advised to advertise only those AYUSH products, which have valid manufacturing license.
Provision of surveillance of AYUSH advertisements has been kept in the central scheme implemented for safety monitoring of Ayurvedic, Siddha, Unani and Homeopathy drugs under the pharmacovigilance initiative.
• Appendicitis • Arteriosclerosis • Blindness • Blood poisoning • Bright’s disease • Cancer • Cataract • Deafness • Diabetes • Diseases and Disorders of brain • Diseases & Disorders of optical system • Diseases and Disorders of the uterus • Disorders of menstrual flow • Disorders of the nervous system • Disorders of the prostatic gland • Dropsy • Epilepsy • Female diseases (in general) • Fevers (in general) • Fits • Form and structure of the female bust • Gall stones, kidney & bladder stones • Gangrene • Glaucoma • Goitre • Heart diseases syphilis, gonorrhoea, soft • High/Low Blood Pressure • Hydrocele • Hysteria • Infantile paralysis • Insanity • Leprosy • Leucoderma • Lockjaw • Locomotor ataxia • Lupus • Nervous debility • Obesity • Paralysis • Plague • Pleurisy • Pneumonia • Rheumatism • Ruptures • Sexual impotence • Smallpox • Stature of persons • Sterility in women • Trachoma • Tuberculosis • Tumours • Typhoid fever • Ulcers of the gastro-intestinal tract • Venereal diseases, including chancre, venereal granuloma and lympho granuloma

Periodic Safety Update Report (PSUR) and Post Marketing Surveillance (4th phase of clinical trial) is described in schedule Y of Drugs & Cosmetic Act 1940 and its rules 1945. Now Government of India, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare on 8th March 2016 published a Gazette Notification under Drugs & Cosmetics Act 1940 and rules 1945 there under included Pharmacovigilance system as a mandate for drugs approved by drug regulatory authorities. The details included in the Gazette Notification G.S.R. 287 (E) are as under:-
The applicant shall have a pharmacovigilance system in place for collecting, processing and forwarding the report to the licensing authority for information on adverse drug reactions emerging from the use of the drugs manufactured or marketed by the applicant in the country.
a) The system shall be managed by qualified and trained personnel and the officer in-charge of collection and processing of data shall be a medical officer or a pharmacist trained in collection and analysis of adverse drug reaction reports.
b) Subsequent to approval of the product, new drug shall be closely monitored for its clinical safety once it is marketed.
c) The applicant shall furnish Periodic Safety Update Reports (PSURs) in order to-

Dr Sunita Vohra makes a presentation on SONAR, giving an insight into need for PV in natural health products An informative symposium-cum-lecture session on pharmacovigilance for herbal medicines was conducted by NCC-PvPI, IPC, Ghaziabad on November 20, 2017. The programme featured Dr Sunita Vohra, Professor, Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Alberta, Canada, who made a presentation on “Study of Natural Health Product Adverse Reactions (SONAR)”. She emphasized the need for pharmacovigilance in herbal products which are essentially natural health products, saying pharmacists must be encouraged to report adverse reactions. She also gave an overview of regulations on natural health products in Canada. The symposium was attended by nearly 30 participants, comprising the licensing and regulatory authority, policy-makers, pharma industry, medical practitioners and academia. Dr. Rubina Bose, DDC (I), CDSCO, Dr Naresh Sharma, ADC (I), CDSCO, were invited as distinguished speakers. Dr Jai Prakash, Senior PSO, IPC, made a presentation on the role of IPC in promoting quality and safety of herbal drugs. The challenges and opportunities in causality assessment of AYUSH drugs were deliberated upon and debated threadbare. The most challenging aspect was reported to be the causality assessment visa-vis the Indian systems of medicine. It was unanimously agreed upon that AYUSH medical colleges be enrolled as Adverse drug reaction Monitoring Centres (AMCs) in a systemic manner so that ADRs from herbal medicines and other traditional Indian systems of medicine can be reported and analysed.